P6 scheduling, using Primavera P6 software, is far more than just creating a Gantt chart; it’s about strategically managing complex projects from inception to completion. This guide delves into the powerful features of P6, exploring how its functionalities can streamline workflows, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately, deliver projects on time and within budget.
We’ll cover everything from basic project setup to advanced techniques like resource leveling and risk management, ensuring you gain a comprehensive understanding of this indispensable project management tool.
We’ll walk you through the core functionalities of Primavera P6, demonstrating how to define activities, establish dependencies, and allocate resources effectively. You’ll learn to leverage critical path analysis to identify potential bottlenecks and utilize various scheduling methodologies to adapt to different project needs.
Furthermore, we’ll explore the integration capabilities of P6 with other software, showcasing how seamless data exchange can enhance overall project visibility and collaboration.
Introduction to P6 Scheduling Software
Primavera P6 is a powerful project management software renowned for its robust scheduling capabilities. It’s a critical tool for organizations needing to plan, execute, and monitor complex projects across various industries, from construction and engineering to IT and pharmaceuticals.
Its comprehensive features allow for detailed scheduling, resource allocation, and risk management, contributing to improved project outcomes and enhanced efficiency.Primavera P6’s core functionalities revolve around creating and managing project schedules. This involves defining tasks, setting dependencies, allocating resources, and tracking progress against the baseline schedule.
The software provides a visual representation of the project timeline, enabling users to identify potential delays, bottlenecks, and resource conflicts proactively. Furthermore, it facilitates collaboration among team members, allowing for real-time updates and improved communication.
Core Functionalities of Primavera P6
Primavera P6 offers a wide array of features designed to streamline project management. These include task definition and sequencing, resource management (including leveling and allocation), cost control, progress tracking, and reporting. The software allows users to create detailed work breakdown structures (WBS), define task durations and dependencies, and assign resources to specific tasks.
Integrated cost management tools enable users to track budgets, forecast expenditures, and monitor cost performance. Furthermore, robust reporting capabilities provide insights into project progress, resource utilization, and potential risks. A critical path method (CPM) analysis is automatically performed, highlighting the most crucial tasks impacting project completion.
For instance, in a construction project, P6 can pinpoint which tasks directly affect the overall project duration, allowing for focused attention and resource allocation.
Project Scheduling Methodologies Supported by P6, P6 scheduling
Primavera P6 supports various project scheduling methodologies, catering to diverse project needs and management styles. These include the critical path method (CPM), which identifies the longest sequence of tasks determining the project duration; and the program evaluation and review technique (PERT), which incorporates uncertainty in task durations through optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely estimates.
Furthermore, P6 can accommodate Agile methodologies by integrating tasks and sprints into the overall project schedule, providing a comprehensive view of both iterative and traditional project management approaches. The flexibility in methodology support allows for adaptation to different project contexts and organizational preferences.
Primavera P6 User Interface and Navigation
The Primavera P6 interface, while initially appearing complex, is logically structured and designed for efficient navigation. The main screen typically displays a calendar view of the project schedule, allowing for quick visual assessment of task progress and potential delays.
Various tabs and menus provide access to different functionalities, including task management, resource allocation, cost control, and reporting. Users can customize the interface to suit their individual preferences, selecting the views and information they need to access most frequently.
Navigation is facilitated through a combination of menus, toolbars, and keyboard shortcuts. The software’s comprehensive help system and online tutorials provide further assistance to users.
Creating a New Project in P6: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a new project in Primavera P6 involves a series of steps designed to ensure comprehensive project setup. First, users need to create a new project file, specifying the project name and other relevant details. Next, they define the project’s work breakdown structure (WBS), breaking down the project into smaller, manageable tasks.
Then, users define task dependencies, specifying the sequence in which tasks must be completed. Following this, resources are assigned to each task, along with estimated durations. Finally, the project schedule is reviewed and adjusted as needed to optimize resource allocation and minimize potential delays.
This process establishes a solid foundation for effective project planning and execution, setting the stage for successful project completion. For example, a software development project might be broken down into phases such as requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, and deployment, with each phase containing several individual tasks.
Defining Project Activities and Relationships
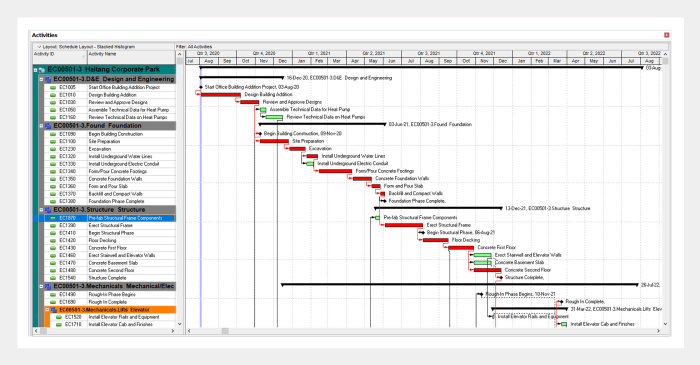
Project scheduling in Primavera P6 hinges on accurately defining individual project activities and their interdependencies. This crucial step lays the foundation for a realistic and effective project plan, allowing for accurate resource allocation, cost estimation, and risk management. Understanding how to define activities, their durations, and relationships is paramount to successful project execution.
Defining Activities and Durations
Within P6, defining an activity involves assigning a unique identifier, a descriptive name, and specifying its duration. The activity name should clearly articulate the task’s purpose. Duration is typically expressed in days, weeks, or months, depending on the project’s scale and preferred time unit.
P6 offers flexibility in defining duration; you can input a fixed duration, or use more advanced techniques like estimating duration based on resource allocation or using statistical distributions for more probabilistic scheduling. Accurate duration estimation is vital for accurate project completion date prediction.
For instance, if a “Foundation Construction” activity is estimated to take 14 days, this information is directly inputted into the activity’s properties within the P6 software.
Activity Relationships
Activity relationships define the dependencies between tasks, outlining the sequence in which they must be performed. P6 supports several relationship types, each with specific implications for scheduling.Finish-to-Start (FS): This is the most common relationship type. A successor activity cannot begin until its predecessor activity is completed.
For example, “Pouring Concrete” (successor) cannot start until “Foundation Construction” (predecessor) is finished.Start-to-Start (SS): The successor activity can begin only after its predecessor activity has started. For instance, “Electrical Wiring” and “Plumbing Installation” might have an SS relationship, meaning both can commence concurrently once the “Rough-In” phase starts.Finish-to-Finish (FF): The successor activity cannot finish until its predecessor activity has finished.
This is less common but useful for activities that must be completed simultaneously. For example, “Final Inspection” and “Site Cleanup” might have an FF relationship, ensuring both are finished together.Start-to-Finish (SF): The successor activity cannot finish until its predecessor activity has started.
This is the least common relationship type. An example might be a training session that must start before a certain task can be finalized.
Creating a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
A WBS is a hierarchical decomposition of the project into smaller, more manageable tasks. In P6, the WBS is represented through the project’s activity structure. You can create a WBS by organizing activities into logical groupings (e.g., phases, sub-projects).
This structured approach enhances clarity, facilitates better control over project progress, and improves communication among team members. A well-defined WBS simplifies the process of assigning resources and tracking individual tasks. For example, a WBS for building a house might have a top-level activity “Construct House,” with sub-activities like “Foundation,” “Framing,” “Roofing,” each further broken down into individual tasks.
Sample Project Schedule
The following table illustrates a sample project schedule with 10 activities and their dependencies:
| Activity ID | Activity Name | Duration (Days) | Predecessors |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Project Initiation | 2 | – |
| B | Requirements Gathering | 5 | A |
| C | Design | 7 | B |
| D | Development | 14 | C |
| E | Testing | 5 | D |
| F | Deployment | 3 | E |
| G | Documentation | 4 | D |
| H | Training | 2 | F |
| I | Go-Live Support | 7 | F,G |
| J | Project Closure | 1 | I,H |
Resource Allocation and Management
Effective resource allocation is the cornerstone of successful project delivery. In Primavera P6, this crucial process involves assigning the right resources—people, equipment, materials—to the right tasks at the right time, optimizing their utilization and minimizing potential conflicts or delays.
Understanding resource types and employing appropriate allocation methods are vital for achieving project goals within budget and schedule constraints.
Assigning Resources to Activities
Assigning resources in P6 typically involves navigating to the resource sheet or the activity sheet, identifying the specific activity, and then selecting the appropriate resource from the available pool. The process involves specifying the resource units assigned, the start and end dates of their involvement, and potentially other relevant parameters like cost rates or specific skills.
For example, if a construction project requires three carpenters for the framing phase, this would be reflected in the assignment, specifying the number of carpenters, their assigned cost rates, and the duration of their involvement in the framing activity.
P6 then automatically updates the activity’s resource requirements and associated costs. Careful consideration of resource availability and potential conflicts is crucial during this assignment process.
Resource Types and Allocation Methods
P6 supports various resource types, including labor (e.g., engineers, architects, construction workers), equipment (e.g., cranes, bulldozers, trucks), and materials (e.g., concrete, lumber, steel). Allocation methods vary depending on the resource type and project requirements. For labor resources, one might use a unit-based allocation, assigning a specific number of workers to an activity.
For equipment, allocation could be based on the number of units required or the total hours of operation. Materials allocation often involves specifying quantities needed at specific times. The choice of allocation method significantly impacts resource utilization and project costs.
Using the wrong method can lead to over-allocation (resource overload) or under-allocation (delays due to insufficient resources).
Resource Leveling and Smoothing
Resource leveling and smoothing are crucial techniques for managing resource utilization. Resource leveling aims to redistribute resources across activities to minimize peak demands and prevent resource over-allocation. This often involves delaying some activities without affecting the overall project completion date.
Resource smoothing, on the other hand, attempts to balance resource utilization without extending the project schedule. It prioritizes efficient resource use while maintaining the original project timeline. P6 provides tools to automatically perform leveling and smoothing, allowing project managers to visualize the impact of these adjustments on both resource utilization and project duration.
For instance, a project might have a high demand for electricians during a specific week. Leveling might redistribute the electrician’s workload to adjacent weeks, preventing a bottleneck.
Best Practices for Resource Optimization
Effective resource optimization involves a proactive approach, starting with accurate resource estimation and realistic scheduling. This includes identifying potential resource conflicts early on and implementing strategies to mitigate them. Regular monitoring of resource utilization and proactive communication with the resource team are essential.
Utilizing P6’s reporting and analysis features provides valuable insights into resource allocation, enabling informed decision-making and adjustments as needed. Moreover, establishing clear roles and responsibilities for resource management within the project team enhances accountability and improves overall efficiency.
For example, regular progress meetings that address resource allocation and potential problems are crucial for maintaining a smooth workflow and preventing costly delays.
Scheduling Techniques and Calculations
Mastering project scheduling involves understanding and applying various techniques to accurately estimate timelines and resource allocation. Effective scheduling hinges on the ability to identify critical paths, manage potential delays, and optimize resource utilization. This section delves into the core scheduling methodologies and calculations crucial for successful project management within Primavera P6.
Critical Path Method (CPM) in P6
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a powerful technique used to determine the shortest possible duration for completing a project. It identifies the sequence of activities that directly influence the overall project duration, known as the critical path. Any delay in these critical path activities directly impacts the project’s completion date.
In Primavera P6, the CPM algorithm automatically calculates the critical path by analyzing activity durations and dependencies. The software visually highlights the critical path, allowing project managers to easily identify and focus on the most time-sensitive tasks. For example, in a construction project, the critical path might involve foundation laying, structural framing, and roofing—delays in any of these directly impact the project completion date.
P6 facilitates this analysis by providing clear visual representations and detailed reports.
Float/Slack in Project Scheduling
Float, also known as slack, represents the amount of time an activity can be delayed without affecting the overall project duration. Activities with zero float are on the critical path. Understanding float is vital for effective resource allocation and risk management.
Activities with significant float offer flexibility for scheduling adjustments, while those with little or no float require close monitoring and proactive management to prevent delays. P6 automatically calculates and displays float for each activity, enabling project managers to make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and potential schedule changes.
A construction project might have activities like interior painting that have significant float, allowing for flexibility in scheduling depending on other tasks’ completion.
P6’s Calculation of Project Duration and Critical Path
Primavera P6 employs sophisticated algorithms to calculate the project duration and identify the critical path. The software considers activity durations, dependencies (finish-to-start, start-to-start, finish-to-finish, start-to-finish), and resource constraints to determine the shortest possible project completion time. The calculation process involves a forward pass (calculating early start and finish times) and a backward pass (calculating late start and finish times).
The difference between early and late start/finish times determines the float. Activities with zero float constitute the critical path. P6 provides comprehensive reports illustrating these calculations, allowing for detailed analysis of the project schedule. For instance, if an activity’s early start is 10 days and its late start is also 10 days, it indicates zero float and therefore lies on the critical path.
Comparison of Scheduling Methods: Critical Chain vs. Critical Path
While the Critical Path Method focuses on activity durations, the Critical Chain Method (CCM) incorporates resource constraints and considers the uncertainties associated with individual tasks. CCM buffers are strategically placed to mitigate the impact of uncertainties and improve project predictability.
Unlike CPM, which primarily focuses on task dependencies, CCM considers resource availability and potential disruptions. P6 can be adapted to accommodate CCM principles, although it doesn’t directly implement CCM algorithms. Project managers often use P6 to simulate different scenarios, considering resource limitations and uncertainties, to reflect CCM principles in their planning and management.
For example, a software development project using CCM might allocate buffers to account for potential delays in coding or testing, which are less easily modeled in a pure CPM approach.
Tracking Progress and Reporting: P6 Scheduling
Effective project tracking and reporting are crucial for maintaining project health and ensuring successful completion. In Primavera P6, these functionalities allow for real-time monitoring, proactive issue identification, and informed decision-making. By accurately reflecting project status, these reports provide a clear picture of performance against the baseline schedule, enabling timely corrective actions.
Updating Project Progress in P6
Updating project progress in Primavera P6 involves recording the actual work completed against the planned schedule. This is typically done by entering the percent complete for each activity or by updating the actual start and finish dates. The system then automatically calculates the earned value, schedule variance, and other key performance indicators (KPIs).
Regular updates, ideally on a weekly or bi-weekly basis, ensure the project schedule remains accurate and reflects the current reality. The frequency of updates should align with the project’s complexity and criticality. For instance, a high-risk, fast-paced project might necessitate daily updates, while a less complex project could be updated weekly.
Inconsistency in updating can lead to inaccurate reporting and compromised decision-making.
Creating Various Reports
Primavera P6 offers a wide range of built-in report types to visualize project data. The Gantt chart remains the cornerstone, providing a visual representation of the project schedule, showing activities, durations, dependencies, and progress. A resource histogram illustrates resource utilization over time, highlighting potential over-allocation or under-utilization.
These reports are easily generated by selecting the desired report type from the reporting menu and specifying the required parameters, such as the project, timeframe, and level of detail. The flexibility of P6 allows for the tailoring of these reports to suit specific needs, offering various levels of granularity and customization options.
For example, one can focus on specific resources or activity types within the report parameters.
Custom Report: Critical Path Activities and Associated Risks
A custom report highlighting critical path activities and their associated risks can be designed using P6’s reporting capabilities. This report enhances risk management by directly linking potential delays to their impact on the overall project schedule. Below is an example of such a report, which can be created by selecting appropriate fields and filters within the custom report generator in P6.
| Activity ID | Activity Name | Duration (Days) | Start Date | Finish Date | Critical? | Associated Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | Foundation Laying | 10 | 2024-03-01 | 2024-03-10 | Yes | Adverse weather conditions, material delays |
| B2 | Wall Construction | 15 | 2024-03-11 | 2024-03-25 | Yes | Labor shortages, equipment malfunction |
| C3 | Roof Installation | 7 | 2024-03-26 | 2024-04-01 | Yes | Supplier issues, unexpected design changes |
Generating Progress Reports and Communicating Project Status
Generating regular progress reports is essential for transparent communication and stakeholder management. P6 allows for the scheduling of automated report generation, ensuring timely distribution. These reports should concisely summarize project progress, highlight key achievements, identify challenges, and Artikel any necessary corrective actions.
Effective communication strategies include regular project meetings, email updates, and visual dashboards that display key performance indicators (KPIs). The communication method should be tailored to the audience and their preferred communication style. For example, executive summaries can be provided to senior management, while detailed progress reports might be circulated among the project team.
This ensures that all stakeholders are informed and aligned with the project’s current status.
Closing Summary
Ultimately, mastering P6 scheduling empowers project managers to navigate complexity with confidence. By understanding the software’s capabilities and applying the techniques discussed in this guide, you can significantly improve project predictability, reduce risks, and achieve better outcomes. From basic project setup to advanced features, this guide provides a solid foundation for utilizing P6 to its full potential, transforming your approach to project management and ultimately, leading to successful project delivery.
